 |
RT-Thread RTOS
An open source embedded real-time operating system
|
 |
RT-Thread RTOS
An open source embedded real-time operating system
|
In order to adapt to more network protocol stack types and avoid the system's dependence on a single network protocol stack, the RT-Thread system provides a SAL (Socket Abstraction Layer) components that implement different network protocol stacks or network implementations. The abstraction of the interface provides a set of standard BSD Socket APIs to the upper layer, so that developers only need to care about and use the network interface provided by the network application layer, without concern for the underlying specific network protocol stack type and implementation, which greatly improves the system's compatibility makes it easy for developers to complete protocol stack adaptation and network-related development. Main features of the SAL component are as follows:
The SAL network framework of RT-Thread is mainly shown in the following structure:
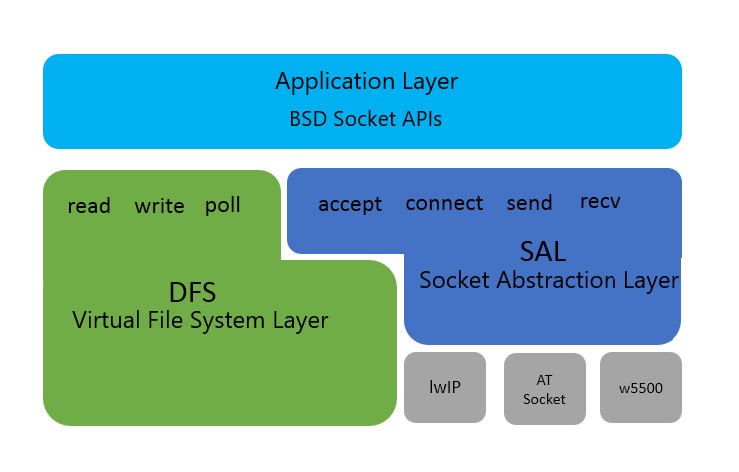
The top layer is the network's application layer, provides a set of standard BSD Socket APIs, such as socket, connect and other functions, for most of the system network development applications.
The second part is the virtual file system layer. In the RT-Thread system, the DFS file system program can implement different file system operations using standard interface functions.The network socket interface also supports the file system structure. The network socket descriptor created when using the network socket interface is uniformly managed by the file system. Therefore, the network socket descriptor can also use the standard file operation interface.The interfaces provided for the upper application layer are: read, write, close, poll/select, and so on.
The third part is the socket abstraction layer, through which RT-thread system can adapt to different network protocol stacks in the lower layer and provide unified network programming interface in the upper layer to facilitate access of different protocol stacks. The socket abstraction layer provides interfaces for the upper application layer, such as accept, connect, send, recv, etc.
The fourth part is the protocol stack layer, which includes several commonly used TCP/IP protocol stacks, such as lwIP, a light TCP/IP protocol stack commonly used in embedded development, and AT Socket network function implementation developed by rt-thread. These protocol stacks or network functions directly contact the hardware to complete the transformation of data from the network layer to the transmission layer.
The network application layer of RT-thread provides interfaces mainly based on the standard BSD Socket API, which ensures that programs can be written on PC, debugged, and then ported to the RT-thread operating system.
The working principle of SAL component is mainly divided into the following three parts:
For different protocol stacks or network function implementations, the names of network interfaces may be different. Take the connect connection function as an example. The interface name in the lwIP protocol stack is lwip_connect, and the interface name in the AT Socket network implementation is at_connect. The SAL component provides abstraction and unification of the interface of different protocol stacks or networks. When the socket is created, the component judges the protocol stack or network function used by judging the incoming protocol domain type, and completes the RT-Thread.
Currently, the protocol stack or network implementation types supported by the SAL component are: lwIP protocol stack, AT Socket protocol stack, WIZnet hardware TCP/IP protocol stack.
The above is the definition of the socket creation function in the standard BSD Socket API. The domain indicates that the protocol domain is also called the protocol domain. It is used to determine which protocol stack or network implementation to use. The domain type used by the AT Socket protocol stack is AF_AT, lwIP protocol stack uses protocol domain type AF_INET, etc., WIZnet protocol stack uses protocol domain type AF_WIZ.
For different software packages, the protocol domain type passed to the socket may be fixed and will not change depending on how the SAL component is accessed. In order to dynamically adapt access to different protocol stacks or network implementations, the SAL component provides two protocol domain type matching methods for each protocol stack or network implementation: Primary protocol domain type and secondary protocol domain type. When socket is created, it first determines whether the incoming protocol domain type has the supported primary protocol type. If it is, it uses the corresponding protocol stack or network implementation, if not, determine whether the subprotocol cluster type supports. The current system support protocol domain types are as follows:
The main function of the SAL component is to unify the underlying BSD Socket API interface. The following takes the connect function call flow as an example to illustrate the SAL component function call method:
connect: The abstract BSD Socket API provided by the SAL component for unified FD management;sal_connect: The connect implementation function in the SAL component that is used to call the operation function registered by the underlying stack.。lwip_connect: The layer connect connection function provided by the underlying protocol stack is registered in the SAL component when the NIC is initialized, and the final call operation function。1. SAL TLS Feature
In the transmission of protocol data such as TCP and UDP, since the data packet is plaintext, it is likely to be intercepted and parsed by others, which has a great impact on the secure transmission of information. In order to solve such problems, users generally need to add the SSL/TLS protocol between the application layer and the transport layer.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a protocol based on the transport layer TCP protocol. Its predecessor is SSL (Secure Socket Layer). Its main function is to encrypt the application layer message asymmetrically and then transmit it by TCP protocol, so as to achieve secure data encryption interaction.
Currently used TLS methods: MbedTLS, OpenSSL, s2n, etc., but for different encryption methods, you need to use their specified encryption interface and process for encryption, the migration of some application layer protocols is more complicated. Therefore, the SAL TLS function is generated, the main function is to provide TLS-encrypted transmission characteristics at the Socket level, abstract multiple TLS processing methods, and provide a unified interface for completing TLS data interaction.
2. How to use the SAL TLS feature
The process is as follows:
After the configuration is complete, as long as the protocol type passed in the socket creation uses PROTOCOL_TLS or **PROTOCOL_DTLS **, the standard BSD Socket API interface can be used to complete the establishment of the TLS connection and the data transmission and reception. The sample code is as follows:
When we use the SAL component we need to define the following macro definition in rtconfig.h:
| Macro definition | Description |
|---|---|
| RT_USING_SAL | Enable the SAL function |
| SAL_USING_LWIP | Enable lwIP stack support |
| SAL_USING_AT | Enable AT Socket protocol stack support |
| SAL_USING_TLS | Enable SAL TLS feature support |
| SAL_USING_POSIX | Enable POSIX file system related function support, such as read, write, select/poll, etc. |
Currently, the SAL abstraction layer supports the lwIP protocol stack, the AT Socket protocol stack, and the WIZnet hardware TCP/IP protocol stack. To enable SAL in the system, at least one protocol stack support is required.
The above configuration options can be added directly to the rtconfig.h file or added by the component package management tool Env configuration option. The specific configuration path in the Env tool is as follows:
After the configuration is complete, you can use the scons command to regenerate the function and complete the addition of the SAL component.
配置开启 SAL 选项之后,需要在启动时对它进行初始化,开启 SAL 功能,如果程序中已经使用了组件自动初始化,则不再需要额外进行单独的初始化,否则需要在初始化任务中调用如下函数:
The initialization function is mainly for initializing the SAL component, supporting the component to repeatedly initialize the judgment, and completing the initialization of the resource such as the mutex used in the component. There is no new thread created in the SAL component, which means that the SAL component resource is very small. Currently, the SAL component resource is occupied by ROM 2.8K and RAM 0.6K.
The SAL component abstracts the standard BSD Socket API interface. The following is an introduction to common network interfaces:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| domain | protocol domain type |
| type | protocol type |
| protocol | Transport layer protocol for actual use |
| back | – |
| >=0 | Success, an integer representing the socket descriptor will be returned |
| -1 | Fail |
This function is used to assign a socket descriptor and the resources it USES based on the specified address family, data type, and protocol.
domain ( protocol domain type ):
type ( protocol type ):
| **P**arameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| name | a pointer to the sockaddr structure representing the address to bind to |
| namelen | length of sockaddr structure |
| back | – |
| 0 | success |
| -1 | fail |
This function is used to bind the port number and IP address to the specified socket。
SAL components depend on the netdev components, when using bind () function, can get IP address information through the netdev nic name, is used to create Socket bound to the specified object of network interface card. The following example completes the process of binding the IP address of the network interface card and connecting to the server through the name of the incoming network interface card:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| backlog | represents the maximum number of connections that can wait at a time |
| back | – |
| 0 | success |
| -1 | fail |
This function is used by the TCP server to listen for a specified socket connection。
| Parameter | Descrption |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| addr | represents the maximum number of connections that can wait at a time |
| addrlen | length of client device address structure |
| back | – |
| 0 | success, return the newly created socket descriptor |
| -1 | fail |
When the application listens for connections from other hosts, the connection is initialized with the accept() function, and accept() creates a new socket for each connection and removes the connection from the listen queue.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| name | server address information |
| namelen | server address structure length |
| back | – |
| 0 | successful, return the newly created socket descriptor |
| -1 | fail |
This function is used to establish a connection to the specified socket.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| dataptr | sent data pointer |
| size | length of sent data |
| flags | flags, usually 0 |
| back | – |
| >0 | success, the length of the sent data is returned |
| <=0 | Fail |
This function is commonly used to send data over a TCP connection。
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| mem | received data pointer |
| len | length of received data |
| flags | flags, usually 0 |
| back | – |
| >0 | success, the length of the received data will be returned |
| =0 | the destination address has been transmitted and the connection is closed |
| <0 | fail |
This function is used to receive data over a TCP connection。
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| dataptr | sent data pointer |
| size | length of sent data |
| flags | flags, usually 0 |
| to | target address structure pointer |
| tolen | length of the target address structure |
| return | – |
| >0 | success, the length of the received data will be returned |
| <=0 | fail |
This function is used for UDP connections to send data。
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| mem | received data pointer |
| len | length of data received |
| flags | flags, usually 0 |
| from | received address structure pointer |
| fromlen | length of received address structure |
| back | – |
| >0 | success, return the length of the received data |
| =0 | the receiving address has been transferred and the connection is closed |
| <0 | fail |
This function is used to receive data on a UDP connection。
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | Socket descriptor |
| back | – |
| 0 | success |
| -1 | fail |
This function is used to close the connection and release the resource.。
| Parameter | Descrption |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| how | socket control |
| back | – |
| 0 | fail |
| -1 | success |
This function provides more permissions to control the closing process of the socket.。
How ( socket control ):
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| level | protocol stack configuration options |
| optname | option name to be set |
| optval | set the buffer address of the option value |
| optlen | set the buffer length of the option value |
| back | – |
| =0 | success |
| <0 | fail |
This function is used to set the socket mode and modify the socket configuration options.。
level ( protocol stack configuration options ):
optname ( Option name to be set ):
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| level | protocol stack configuration options |
| optname | option name to be set |
| optval | get the buffer address of the option value |
| optlen | get the buffer length address of the option value |
| back | – |
| =0 | success |
| <0 | fail |
This function is used to get the socket configuration options。
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| name | received address structure pointer |
| namelen | length of received address structure |
| back | – |
| =0 | success |
| <0 | fail |
This function is used to get the remote address information associated with the socket。
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | Socket descriptor |
| name | received address structure pointer |
| namelen | length of received address structure |
| back | – |
| =0 | success |
| <0 | fail |
This function is used to get local socket address information。
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| s | socket descriptor |
| cmd | socket operation command |
| arg | operation command's parameters |
| back | – |
| =0 | success |
| <0 | fail |
This function sets the socket control mode。
The CMD supports following commands
Access to the network protocol stack or network function implementation is mainly to initialize and register the protocol cluster structure, and add it to the protocol cluster list in SAL component. The protocol cluster structure is defined as follows:
family: Each protocol stack supports the main protocol cluster types, such as AF_INET for lwIP, AF_AT Socket, and AF_WIZ for WIZnet。sec_family:The type of sub-protocol domain supported by each protocol stack, used to support a single protocol stack or network implementation, that matches other types of protocol cluster types in the package。skt_ops: Define socket related functions, such as connect, send, recv, etc., each protocol cluster has a different set of implementation。netdb_ops:Define non-socket-related execution functions, such as gethostbyname, getaddrinfo, freeaddrinfo, etc. Each protocol cluster has a different set of implementations。The following is the access registration process implemented by AT Socket network. Developers can refer to other protocol stacks or network implementations for access: